This post is also a topic shared on this WordPress Meetup!
https://www.meetup.com/Taoyuan-WordPress-Meetup/events/270651847/
“How to Do Custom CSS in WordPress” is a question asked frequently. Here are five methods including the best choices for what purposes you’ll need.
Method 1
Custom CSS in WordPress – “Additional CSS” Tab
Starting with WordPress 4.7, you can now add custom CSS to your own theme from the Appearance Customize Screen, without the need for additional plugins or directly editing themes and child themes. Just choose the Additional CSS tab when customizing your current theme to get started!
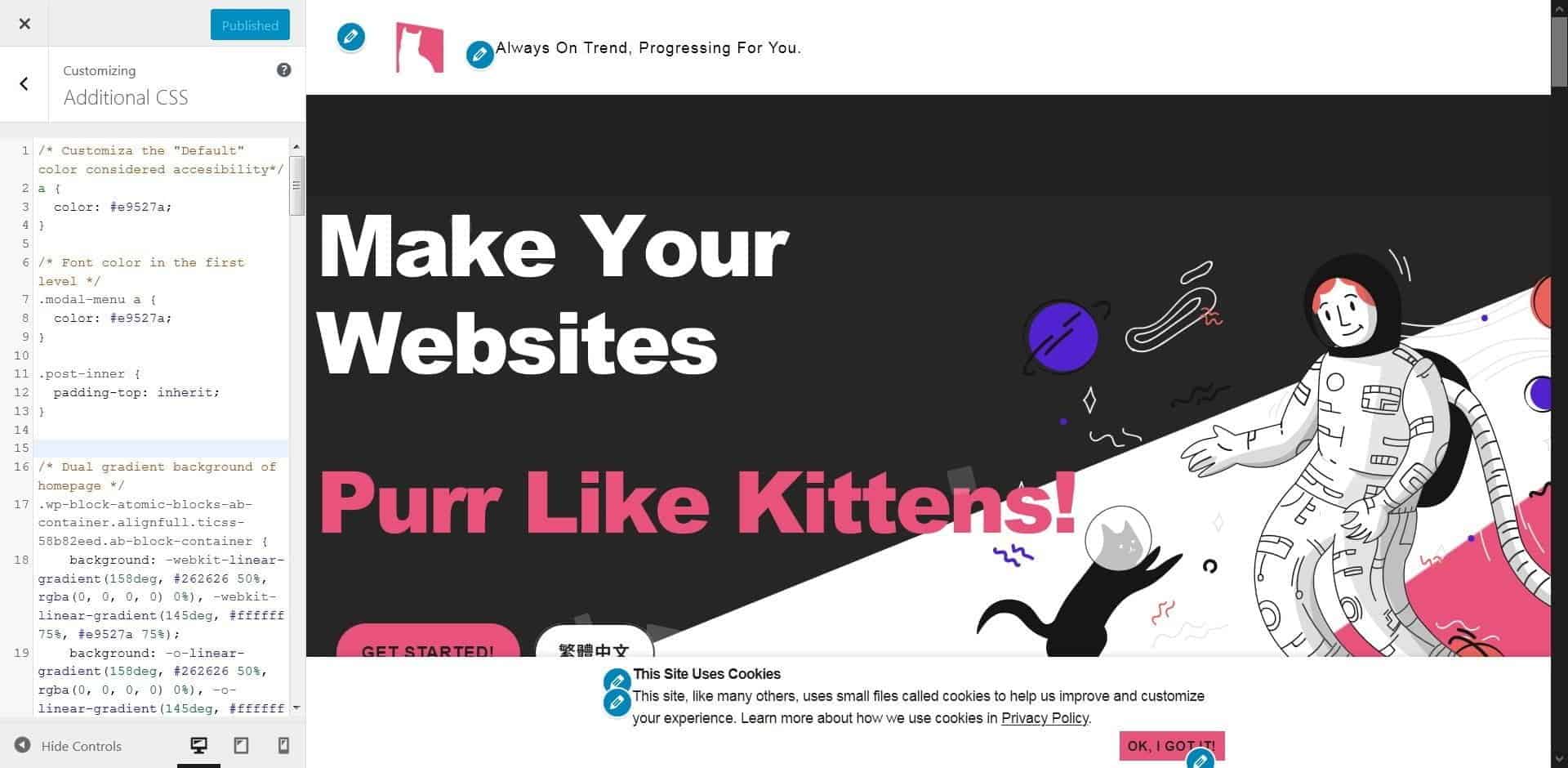
Any CSS changes you make will appear in the preview, just like other changes made in the customizer, this means you have time to tweak and perfect the look of your site, without actually changing anything until you are happy with it all!
VIA Codex, WordPress.ORG
https://codex.wordpress.org/CSS
Keep in mind that the CSS changes are tied in with your theme. This means that if you change to a new theme, your custom CSS styles will no longer be active (of course, if you change back to your previous theme, they will once again be there).
Pros:
- Native, manageable, and easy.
- Could view results immediately without saving.
- Suitable for anyone who has basic CSS knowledge or know how to do copy & paste job if they have the correct source codes.
Cons:
- The field width is fixed and isn’t adjustable.
Pros and cons: Custom CSS follows the activated theme individually.
(Practice Time)
Method 2
Custom CSS in Code Snippets
Code Snippets is an easy, clean, and simple way to run PHP code snippets on your site. It removes the need to add custom snippets to your theme’s functions.php file.
You can run not only PHP but also CSS, JS, and HTML code snippets on your site.
Here are CSS code snippet examples.
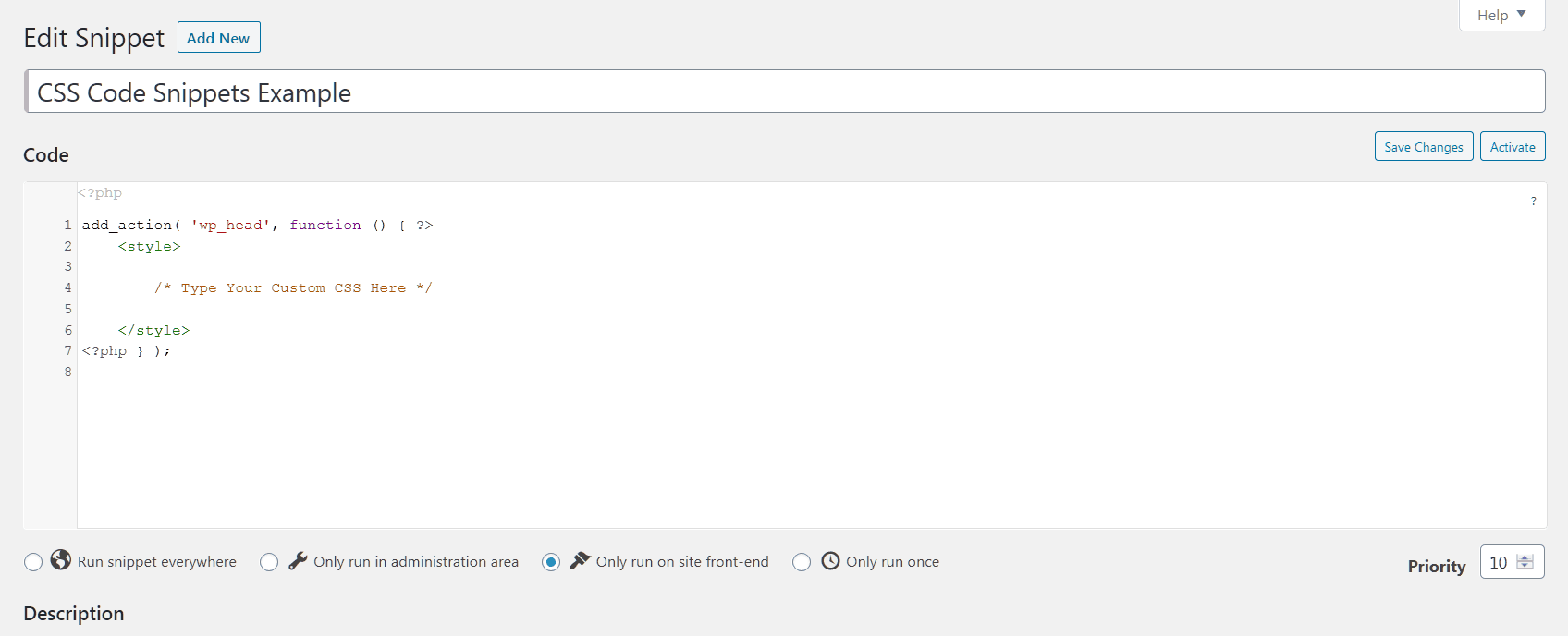
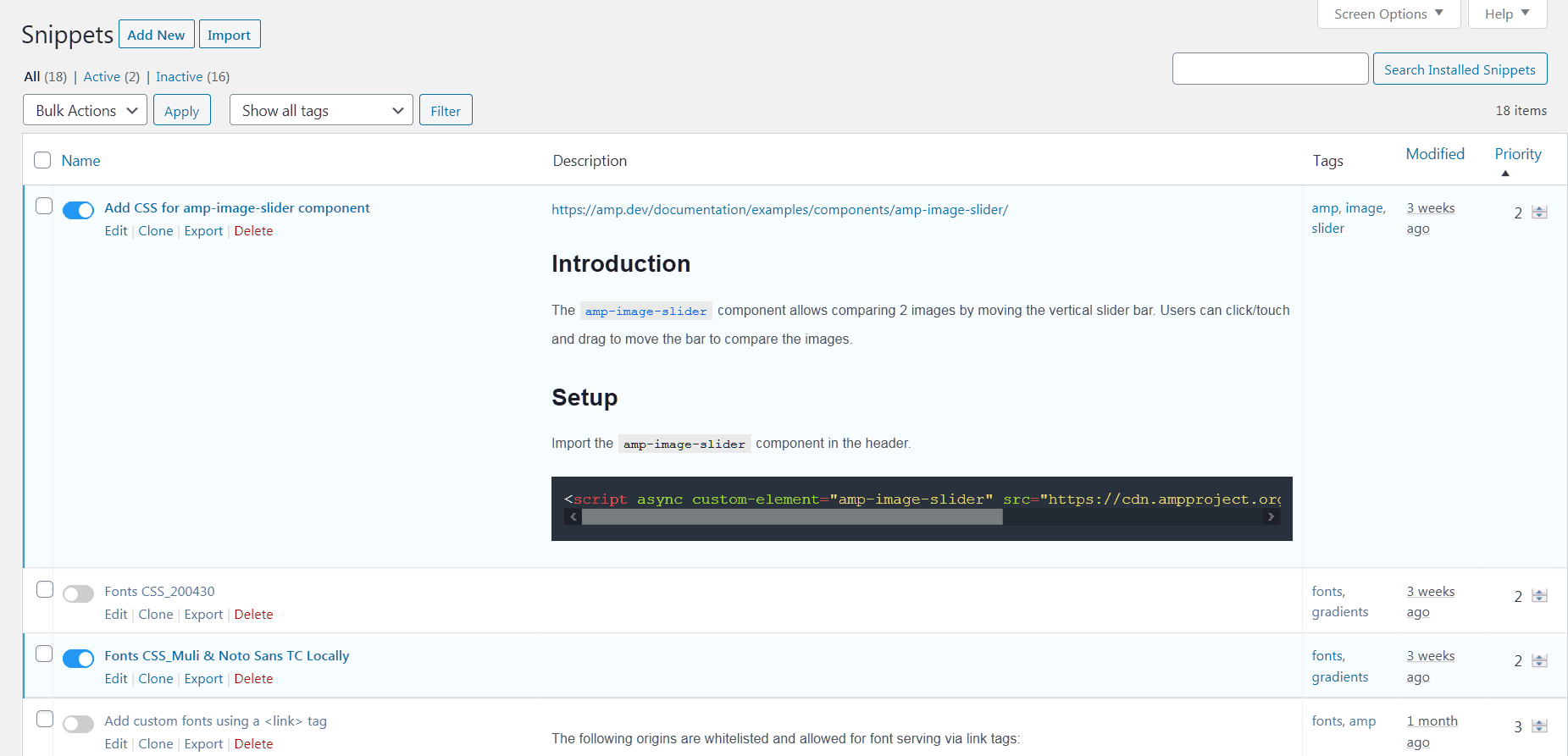
You can also choose a similar plugin for header or footer only.
Pros:
- Manageable, functional, highly flexible, and not so difficult for custom CSS.
- Switches are convenient for testing and developing
Cons:
- Couldn’t view results immediately without saving.
Pros and cons: Custom CSS are independent from any themes.
(Practice Time)
Method 3
Blocks CSS: CSS Editor for Gutenberg Blocks
Blocks CSS allows you add custom CSS to your Gutenberg Blocks straight from the Editor.
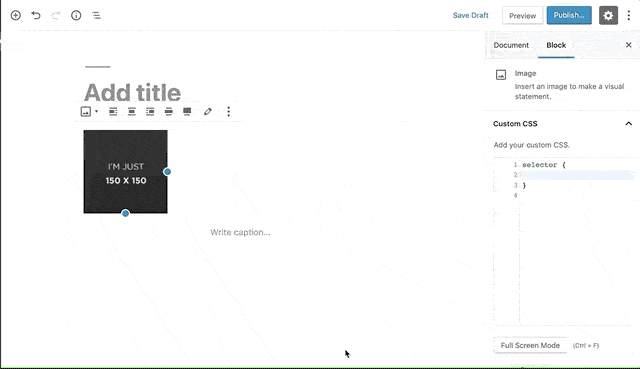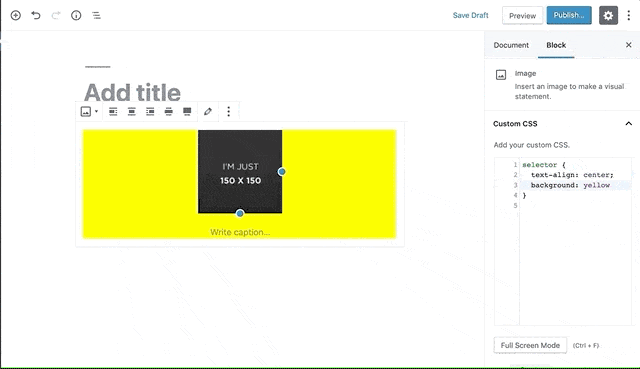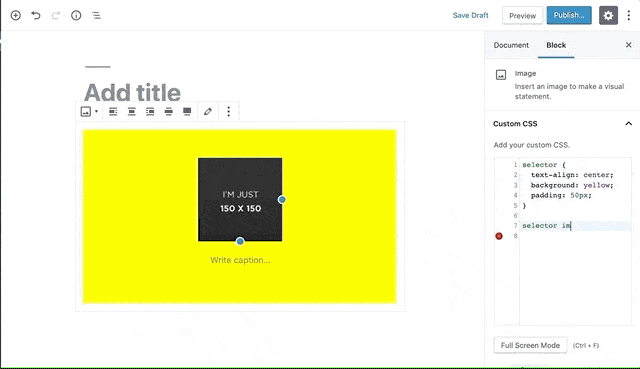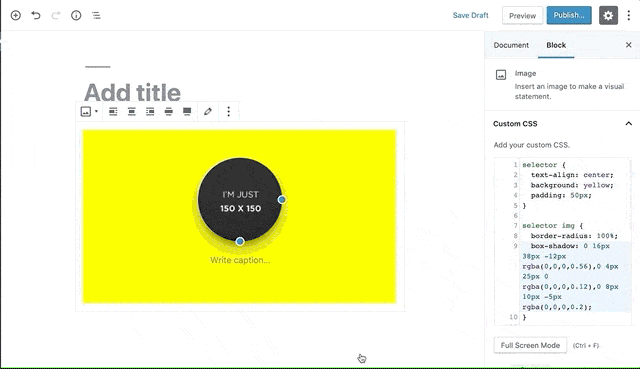
It adds a syntax-highlighted CSS Editor where you can add additional CSS to your Gutenberg Blocks to style them the way you want.
Pros:
- Easy, even lazy.
- Need not know what the exact element name you want to control is.
selector { }is always typed automatically
Cons:
- Unmanageable.
- You might forget what & where the custom CSS codes are.
Pros and cons: Custom CSS are independent from any themes.
Method 4
Custom CSS in Page Editor – Elementor Pro
Add custom CSS to any section, column, widget, or page in Elementor “Pro” version. It means not free to use this function.
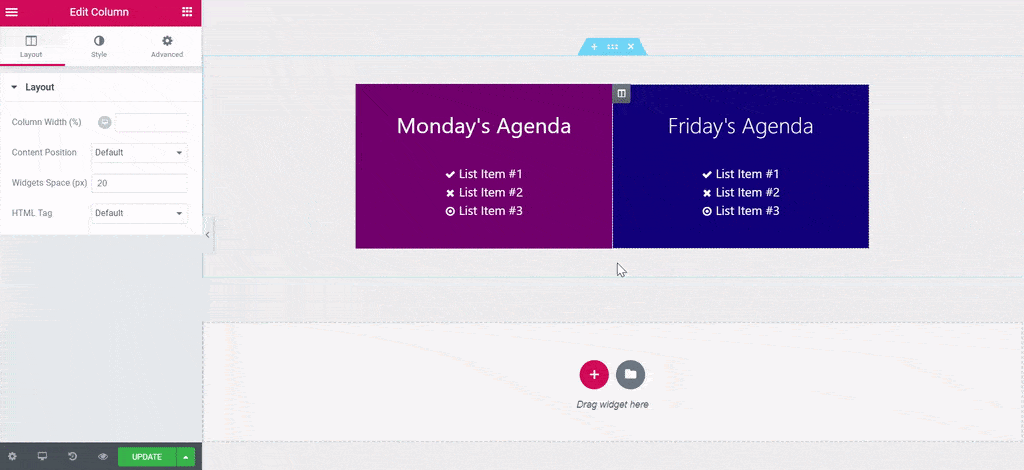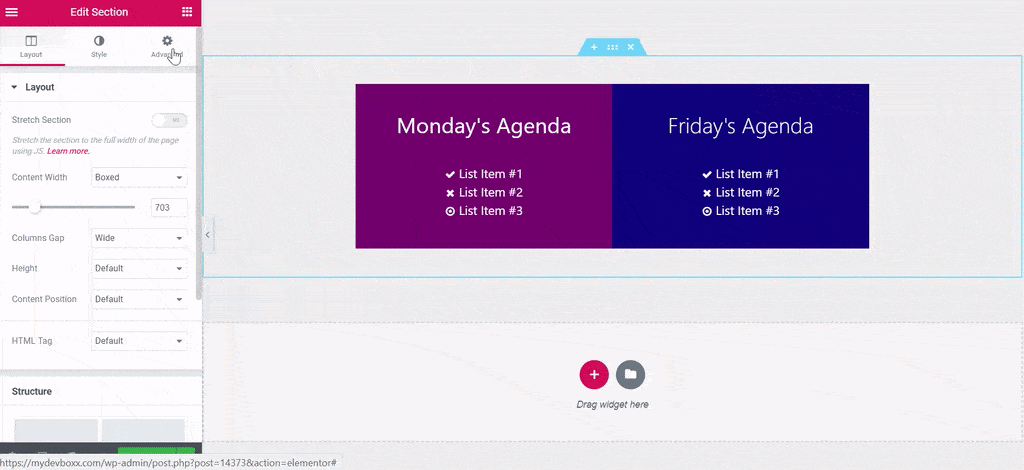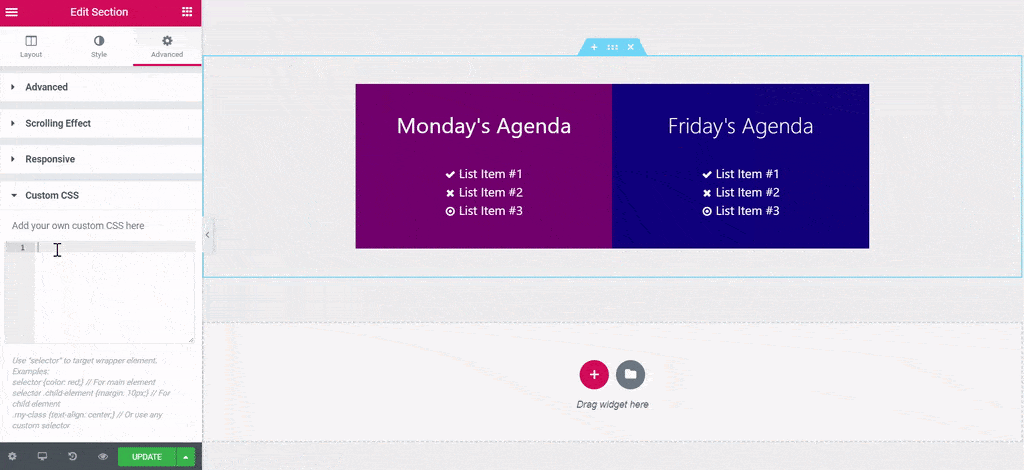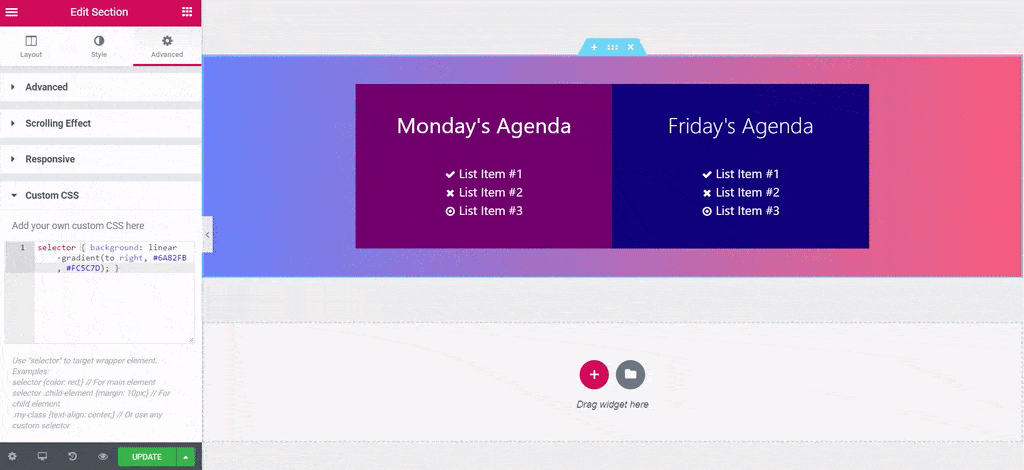
Pros:
- Easy, even lazy.
- Need not know what the exact element name you want to control is.
Cons:
- Unmanageable.
- You might forget what & where the custom CSS codes are.
selector { }is NOT typed automatically, need to type this repeated code manually in every custom CSS field.
Pros and cons: Custom CSS is independent of any themes.
Method 5
Custom CSS in Theme Options of Their Back-end
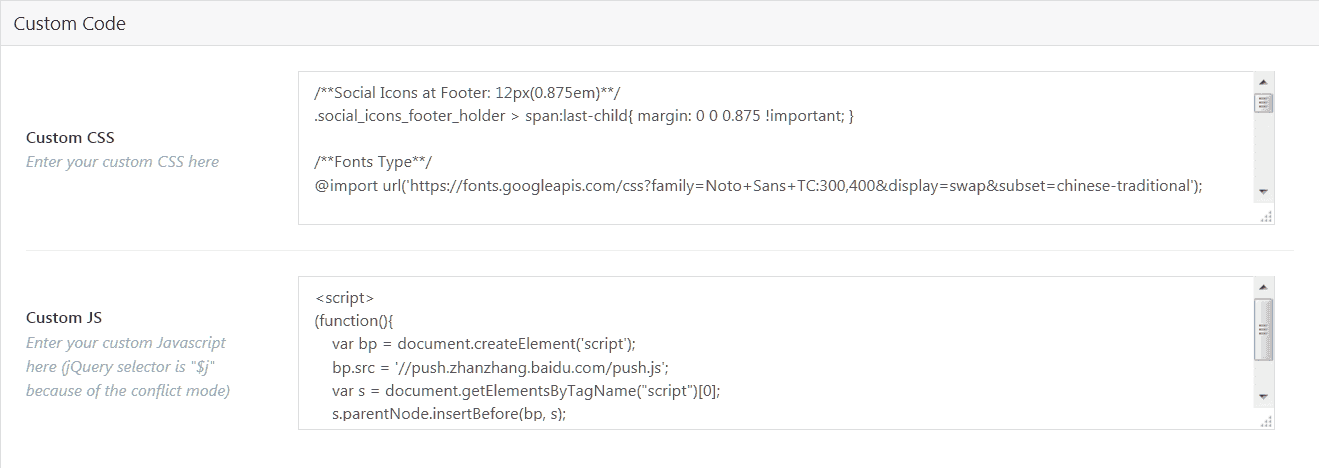
I think its main purpose is not for users to do custom CSS jobs.
It helps users to import demos so that their websites could look like the demo site.
That’s what meaningful it is, I think so.
Pros:
- Manageable and easy.
Cons:
- Couldn’t view results immediately without saving.
- Usually too simple so that’s bad to edit and advanced coding.
Pros and cons: Custom CSS follows the activated theme individually.
Conclusion
Choose one of the top 2 best methods depending on what you and your website development environment need.
- Method 1
Custom CSS in WordPress – “Additional CSS” - Method 2
Code Snippets (or similar plugins like that).
Or choose one of these 2 methods compatible with the editor. Take advantage of skipping the step of checking elements you need if you have no problem with CSS management.
- Method 3
Blocks CSS: CSS Editor for Gutenberg Blocks - Method 4
Custom CSS in Page Editor – Elementor Pro
Then, you will be happy with your website customized by yourself!



